BarnBuster
Virtually Unknown Member
At Rouen in English-controlled Normandy on May 30, 1431, Joan of Arc, the peasant girl who became the savior of France, is burned at the stake for heresy.
Joan was born in 1412, the daughter of a tenant farmer at Domremy, on the borders of the duchies of Bar and Lorraine. In 1415, the Hundred Years War between England and France entered a crucial phase when the young King Henry V of England invaded France and won a series of decisive victories against the forces of King Charles VI. By the time of Henry’s death in August 1422, the English and their French-Burgundian allies controlled Aquitaine and most of northern France, including Paris. Charles VI, long incapacitated, died one month later, and his son, Charles, regent from 1418, prepared to take the throne. However, Reims, the traditional city of French coronation, was held by the Anglo-Burgundians, and the Dauphin (heir apparent to the French throne) remained uncrowned. Meanwhile, King Henry VI of England, the infant son of Henry V and Catherine of Valois, the daughter of Charles VI, was proclaimed king of France by the English.
Joan’s village of Domremy lay on the frontier between the France of the Dauphin and that of the Anglo-Burgundians. In the midst of this unstable environment, Joan began hearing “voices” of three Christian saints—St. Michael, St. Catherine, and St. Margaret. When she was about 16, these voices exhorted her to aid the Dauphin in capturing Reims and therefore the French throne. In May 1428, she traveled to Vaucouleurs, a stronghold of the Dauphin, and told the captain of the garrison of her visions. Disbelieving the young peasant girl, he sent her home. In January 1429, she returned, and the captain, impressed by her piety and determination, agreed to allow her passage to the Dauphin at Chinon.
Dressed in men’s clothes and accompanied by six soldiers, she reached the Dauphin’s castle at Chinon in February 1429 and was granted an audience. Charles hid himself among his courtiers, but Joan immediately picked him out and informed him of her divine mission. For several weeks, Charles had Joan questioned by theologians at Poitiers, who concluded that, given his desperate straits, the Dauphin would be well-advised to make use of this strange and charismatic girl.
Charles furnished her with a small army, and on April 27, 1429, she set out for Orleans, besieged by the English since October 1428. On April 29, as a French sortie distracted the English troops on the west side of Orleans, Joan entered unopposed by its eastern gate. She brought greatly needed supplies and reinforcements and inspired the French to a passionate resistance. She personally led the charge in several battles and on May 7 was struck by an arrow. After quickly dressing her wound, she returned to the fight, and the French won the day. On May 8, the English retreated from Orleans.
During the next five weeks, Joan and the French commanders led the French into a string of stunning victories over the English. On July 16, the royal army reached Reims, which opened its gates to Joan and the Dauphin. The next day, Charles VII was crowned king of France, with Joan standing nearby holding up her standard: an image of Christ in judgment. After the ceremony, she knelt before Charles, joyously calling him king for the first time.
On September 8, the king and Joan attacked Paris. During the battle, Joan carried her standard up to the earthworks and called on the Parisians to surrender the city to the king of France. She was wounded but continued to rally the king’s troops until Charles ordered an end to the unsuccessful siege. That year, she led several more small campaigns, capturing the town of Saint-Pierre-le-Moitier. In December, Charles ennobled Joan, her parents, and her brothers.
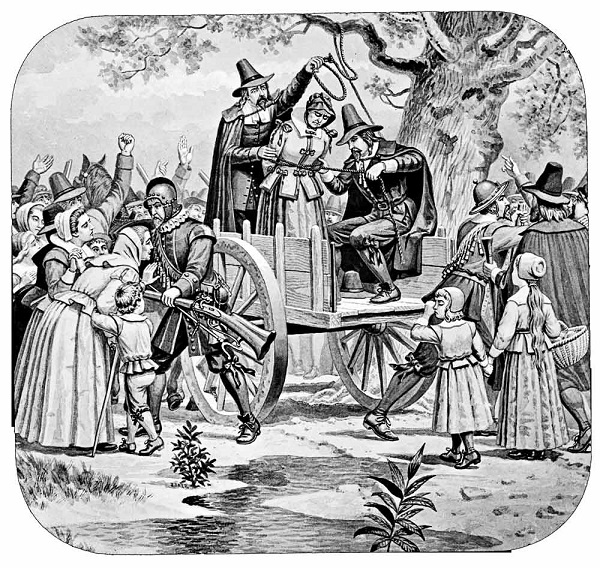
In May 1430, the Burgundians laid siege to Compiegne, and Joan stole into the town under the cover of darkness to aid in its defense. On May 23, while leading a sortie against the Burgundians, she was captured. The Burgundians sold her to the English, and in March 1431 she went on trial before ecclesiastical authorities in Rouen on charges of heresy. Her most serious crime, according to the tribunal, was her rejection of church authority in favor of direct inspiration from God. After refusing to submit to the church, her sentence was read on May 24: She was to be turned over to secular authorities and executed. Reacting with horror to the pronouncement, Joan agreed to recant and was condemned instead to perpetual imprisonment.
Ordered to put on women’s clothes, she obeyed, but a few days later the judges went to her cell and found her dressed again in male attire. Questioned, she told them that St. Catherine and St. Margaret had reproached her for giving in to the church against their will. She was found to be a relapsed heretic and on May 29 ordered handed over to secular officials. On May 30, Joan, 19 years old, was burned at the stake at the Place du Vieux-Marche in Rouen. Before the pyre was lit, she instructed a priest to hold high a crucifix for her to see and to shout out prayers loud enough to be heard above the roar of the flames.
As a source of military inspiration, Joan of Arc helped turn the Hundred Years' War firmly in France’s favor. By 1453, Charles VII had reconquered all of France except for Calais, which the English relinquished in 1558. In 1920, Joan of Arc, one of the great heroes of French history, was recognized as a Christian saint by the Roman Catholic Church. Her feast day is May 30.
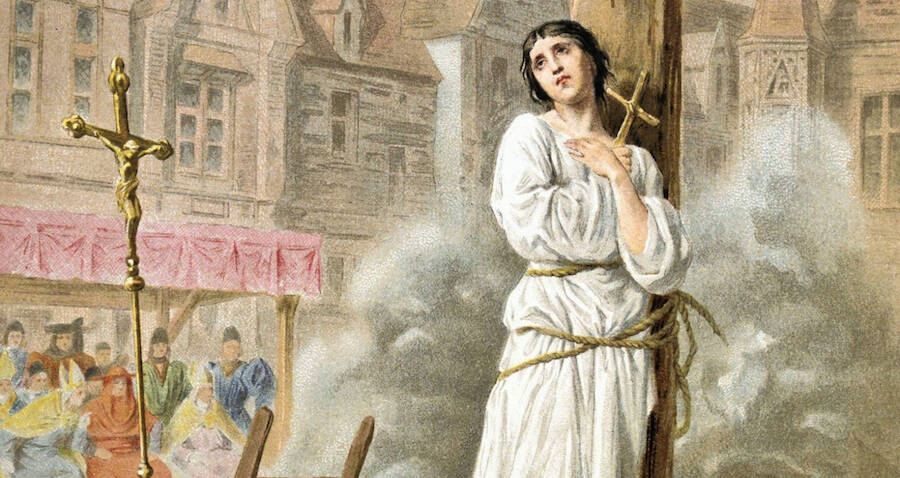

The Sham Trial And Gruesome Death Of Joan Of Arc
Her main offense: cross-dressing.
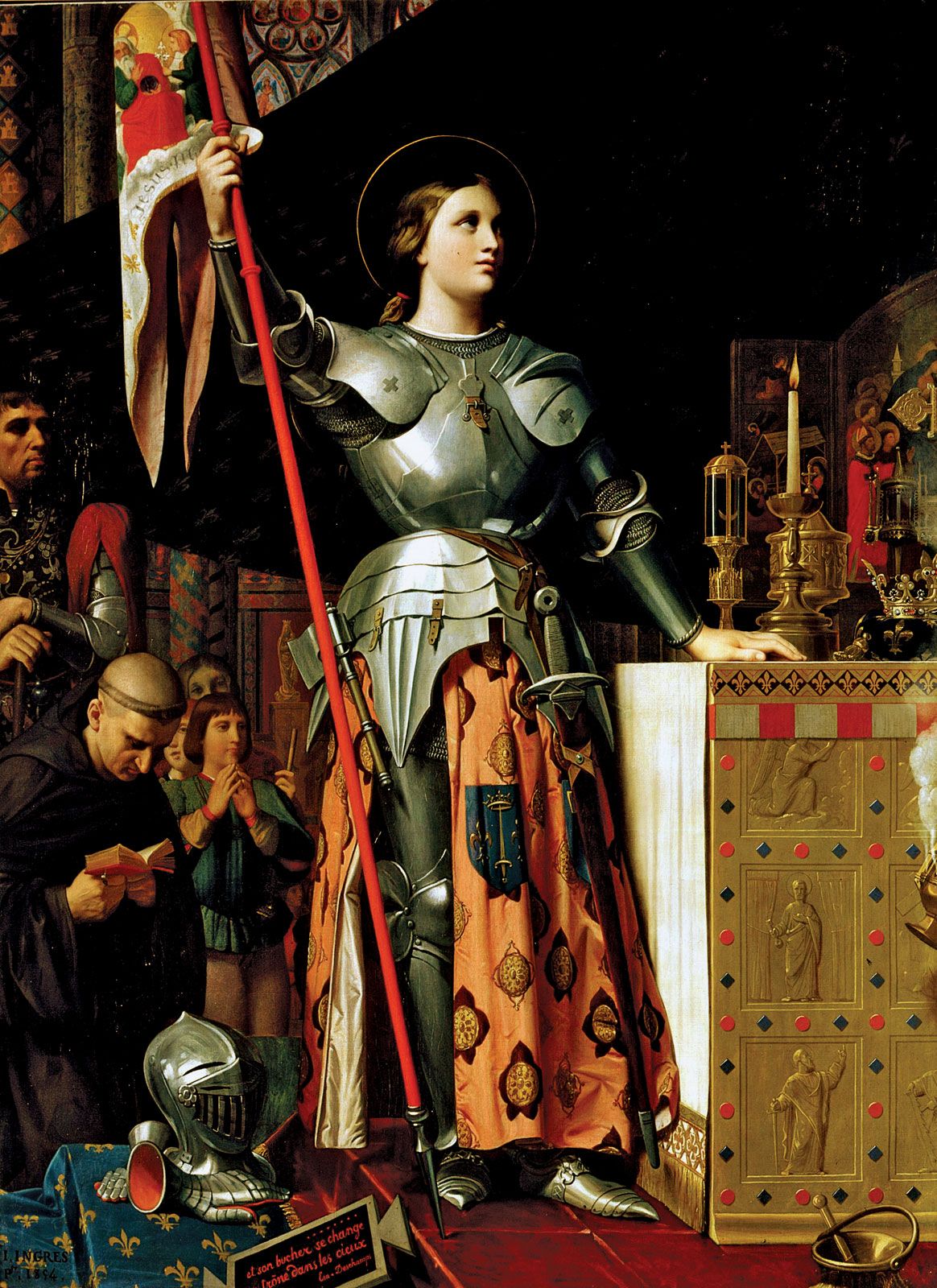

St. Joan of Arc - French Heroine, Military Leader, Martyr | Britannica
St. Joan of Arc - French Heroine, Military Leader, Martyr: Joan of Arc’s place in history is assured. Perhaps her contribution to the history of human courage is greater than her significance in the political and military history of France. She was victimized as much by a French civil conflict...