Brick Top
New Member
And another:
THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF TRICHOME GLANDS
Trichomes are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, also called resin glands. Trichomes can vary in size and structure depending on the plant in question. We are however only interested in the trichomes found on cannabis plants.
There are three known types of glands that occur on the cannabis plant.
They are most heavily concentrated on the floral parts of the female plant:

(Photo by Pistals)
Bulbous
These types of gland are the smallest (15-30 micron across). Anywhere from one to four cells make up the "foot" and "stalk," and one to four cells make up the "head" of the gland. They can be found everywhere on the surface of the plant that is above ground level. Head cells secrete a resin, presumably cannabinoids, and related compounds that accumulate between the head cells and the cuticle.
Capitate – Sessile
The second type of gland is larger (25 to 100 micrometers) and more numerous than the bulbous glands. They are called capitate, which means having a globular-shaped head. On immature plants, the heads lie flush, appearing not to have a stalk and are called capitate sessile. They have a stalk that is one cell high, although it may not be visible beneath the globular head. These cells secrete cannabinoids and related compounds.
Capitate – Stalked
These type of glands appear during flowering and occur especially on the bracts subtending a flower and seed and also small leaves that accompany the flowers. They contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids and can range in size from 150 – 500 microns. The male flowers also have stalked glands, but they are smaller and less concentrated than on the female plant. These resin glands contain the most THC, which is also why they are the most important. Good cannabis plants have mostly capitate-stalked glandular trichomes and in very high concentration.
(The structures pointed out by the red arrow is a cystolith hair that lack the bulbous head of the other trichomes.)
In order to determine the dominant type of trichome on your plant, you will need to look at the female flowers through magnification. Although different plants may seem as frosty as the next, it is actually the dominant type of trichome and the concentration in which it occurs that determines the potency of the final product.
The capitate-stalked glandular trichome changes color as it matures. Newly formed and immature glands are clear, glands reaching optimum THC production are cloudy or milky and amber trichomes have already passed their peak. By looking at the trichomes you can also determine the best time to harvest your plants. When most trichomes have gone cloudy and a few amber ones have appeared, the plant is at its peak.

INSIDE THE TRICHOME
THC and other cannabinoids are produced mostly in one place on the cannabis plant:
inside the heads of the capitate-stalked trichomes.
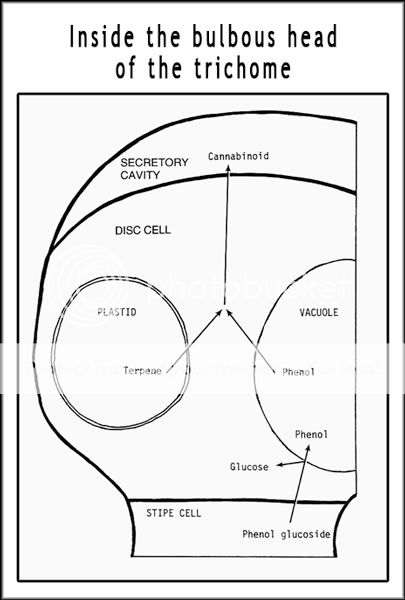
How it happens:
Organelles produced by the plant called Vacuoles - which contain phenols, a chemical compound similar to alcohol and another type of organelle called plastids - containing hydrocarbons called terpenes, make their way up the trichome stalk and combine inside the secretory cavity into a fibrous mat. This concentrated mat is hit by UV-B light waves, causing the creation of cannabinoids. Since all of the psychoactive ingredients are produced inside the trichome, these tiny resin heads have long been sought after by hash and oil makers and can be separated from the plant and harvest in a variety of ways.

Why Trichomes?
Cannabis and many other plants have evolved resin trichomes for variety of uses. They protect the plant from UVB light rays, especially Cannabis plant since THC has very good UV-B light absorption. It protects the plant from insects and animals and also provides protection for buds from low humidity and harsh winds.
THE DIFFERENT TYPES OF TRICHOME GLANDS
Trichomes are fine outgrowths or appendages on plants, also called resin glands. Trichomes can vary in size and structure depending on the plant in question. We are however only interested in the trichomes found on cannabis plants.
There are three known types of glands that occur on the cannabis plant.
They are most heavily concentrated on the floral parts of the female plant:

(Photo by Pistals)
Bulbous
These types of gland are the smallest (15-30 micron across). Anywhere from one to four cells make up the "foot" and "stalk," and one to four cells make up the "head" of the gland. They can be found everywhere on the surface of the plant that is above ground level. Head cells secrete a resin, presumably cannabinoids, and related compounds that accumulate between the head cells and the cuticle.
Capitate – Sessile
The second type of gland is larger (25 to 100 micrometers) and more numerous than the bulbous glands. They are called capitate, which means having a globular-shaped head. On immature plants, the heads lie flush, appearing not to have a stalk and are called capitate sessile. They have a stalk that is one cell high, although it may not be visible beneath the globular head. These cells secrete cannabinoids and related compounds.
Capitate – Stalked
These type of glands appear during flowering and occur especially on the bracts subtending a flower and seed and also small leaves that accompany the flowers. They contain the highest concentration of cannabinoids and can range in size from 150 – 500 microns. The male flowers also have stalked glands, but they are smaller and less concentrated than on the female plant. These resin glands contain the most THC, which is also why they are the most important. Good cannabis plants have mostly capitate-stalked glandular trichomes and in very high concentration.
(The structures pointed out by the red arrow is a cystolith hair that lack the bulbous head of the other trichomes.)
In order to determine the dominant type of trichome on your plant, you will need to look at the female flowers through magnification. Although different plants may seem as frosty as the next, it is actually the dominant type of trichome and the concentration in which it occurs that determines the potency of the final product.
The capitate-stalked glandular trichome changes color as it matures. Newly formed and immature glands are clear, glands reaching optimum THC production are cloudy or milky and amber trichomes have already passed their peak. By looking at the trichomes you can also determine the best time to harvest your plants. When most trichomes have gone cloudy and a few amber ones have appeared, the plant is at its peak.

INSIDE THE TRICHOME
THC and other cannabinoids are produced mostly in one place on the cannabis plant:
inside the heads of the capitate-stalked trichomes.

How it happens:
Organelles produced by the plant called Vacuoles - which contain phenols, a chemical compound similar to alcohol and another type of organelle called plastids - containing hydrocarbons called terpenes, make their way up the trichome stalk and combine inside the secretory cavity into a fibrous mat. This concentrated mat is hit by UV-B light waves, causing the creation of cannabinoids. Since all of the psychoactive ingredients are produced inside the trichome, these tiny resin heads have long been sought after by hash and oil makers and can be separated from the plant and harvest in a variety of ways.

Why Trichomes?
Cannabis and many other plants have evolved resin trichomes for variety of uses. They protect the plant from UVB light rays, especially Cannabis plant since THC has very good UV-B light absorption. It protects the plant from insects and animals and also provides protection for buds from low humidity and harsh winds.
